Polymers – Solvent Swelling and Interactions
Polymers are often categorized by their stability and functionality, which are designed to maximize their performance. The ability to measure and quantify performance is essential in optimizing formulations and furthering development.
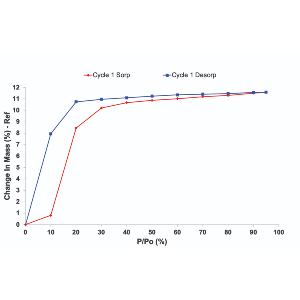
Polymer surfaces are inherently heterogeneous due to varying topography, contamination from organics, and unpolymerized monomers. These macromolecules are likely to interact with liquids via surface interaction (adsorption) and with the bulk of the polymer (absorption). Solvents and moisture can penetrate a polymer matrix often causing them to swell, vastly altering its surface area to volume ratio. Changes to the surface of a polymer can drastically change its surface area, surface energy, and overall activity.