BET Surface Area Measurements by Sorption Methods at Ambient Conditions
Watch now
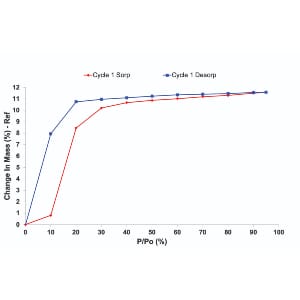
Traditional BET surface area measurements are typically performed by volumetric, gas sorption techniques. These methods require exposing the material of interest to very low pressures (10-3 Torr and below) and cryogenic temperatures (77K). These conditions can have deleterious affects on many classes of materials; including pharmaceuticals, foods, cellulose-based samples, and natural ingredients. In particular, low pressures and temperatures can cause structure collapse or phase changes on fragile solids.
Flow-based sorption techniques, like Dynamic Vapor Sorption (DVS) and Inverse Gas Chromatography (IGC) can be performed at atmospheric pressure and room temperature. These techniques can be used to determine BET surface areas at industrially relevant and environmental storage conditions. In addition, these techniques can be performed over a wide range of relative humidity conditions, which allow surface characterization and determination of surface areas at ‘real-world’ conditions.
This educational seminar overviews the BET surface area principle by DVS and IGC. Also, it compares results with volumetric measurements and highlight the application of DVS and IGC surface area measurements on a range of materials.
Dr. Daniel Burnett
Vice President
Surface Measurement Systems NA