Knowledge hub
Welcome to the Surface Measurement Systems Knowledge Hub. Here you can find a variety of useful resources for using our instruments and sorption science.
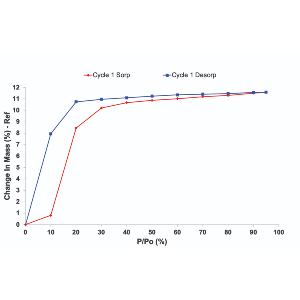
Access our full range of application notes, containing essential information for setting up and running sorption experiments across a range of industrial applications, as well as case studies and technical notes for using your SMS instrument. Also access a collection of informative webinars and instructional videos to build your knowledge and expertise.
Looking for the Sorption Hub customer portal? You can access it here.
Downloads
Discover more about our full range of instruments with our product brochures, and gain detailed insight into the application of sorption science with our full range of Application Notes, Case Studies, and Technical Notes.
Videos
From practical demonstrations to a large catalogue of informative webinars, this collection of sorption science videos will give you all the practical and theoretical knowledge you could need to run experiments on your SMS instrument.

Discover the power of sorption instrumentation
Surface Measurement Systems develops and manufactures the world’s leading gravimetric sorption analyzers. To find out more about our DVS and iGC instruments, use the link below to view our full range.